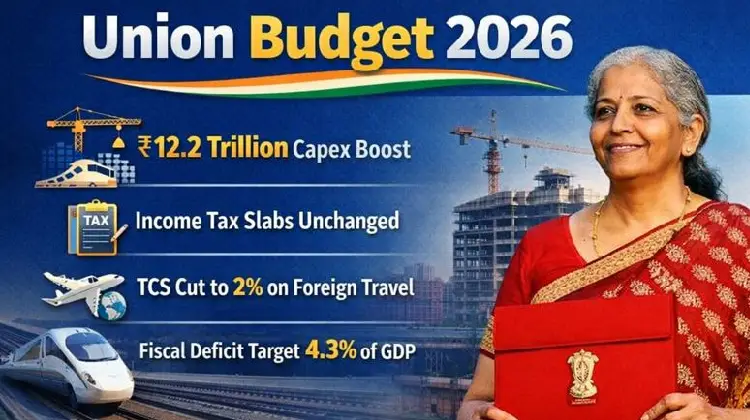
In a landmark Sunday session on February 1, 2026, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented her record ninth consecutive Union Budget, steering India toward a “future-ready Bharat” with a massive infrastructure push. The budget for FY 2026-27 prioritizes long-term growth and fiscal discipline, raising the capital expenditure (capex) outlay to ₹12.2 lakh crore, an 8.9% increase from the previous year. While the middle class saw no changes to income tax slabs, the government introduced a suite of reforms aimed at simplifying compliance and boosting domestic manufacturing.
Infrastructure and Strategic Corridors
The government has doubled down on its infrastructure-led growth strategy, allocating significant funds to connectivity and industrial depth.
- Rare Earth Corridors: Dedicated corridors will be established in Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Odisha, and Andhra Pradesh to secure critical mineral supply chains.
- Rail & Waterways: Plans include seven high-speed rail corridors and 20 new national waterways to slash logistics costs.
- City Economic Regions (CER): An allocation of ₹5,000 crore per city over five years was announced to transform Tier-2 and Tier-3 centers into growth hubs.
Tax Reforms and Middle-Class Relief
Despite holding steady on tax slabs, the Finance Minister proposed several “ease of living” measures:
- New Income Tax Act, 2025: Set to take effect on April 1, 2026, the new act aims to simplify the code and reduce litigation.
- ITR Flexibility: The deadline for revising Income Tax Returns (ITR) has been extended to March 31, providing more breathing room for taxpayers.
- TCS Reductions: In a major win for travelers and students, the TCS on overseas tour packages and foreign medical/educational remittances has been slashed to 2% from the previous 5-20% range.
- STT Hike: To curb hyper-speculation in the derivatives market, the Securities Transaction Tax (STT) on futures has been raised to 0.05% and on options to 0.15%, a move that briefly rattled the stock market.
Manufacturing and Emerging Sectors
Under the “Challenge Route” and “Mission Mode” initiatives, the budget targets self-reliance in high-tech industries.
- Semiconductors: The launch of ISM 2.0 (India Semiconductor Mission) signals continued focus on chip design and manufacturing.
- Biopharma & Chemicals: A ₹10,000 crore allocation for the biopharma sector and the creation of cluster-based chemical parks in every state are set to drive industrial expansion.
- MSME Support: A new ₹10,000 crore SME Growth Fund was introduced to help small businesses scale into global champions.
Fiscal Prudence
Maintaining its path of fiscal consolidation, the government expects the fiscal deficit to narrow to 4.3% of GDP for FY27. Total expenditure for the year is pegged at ₹53.5 lakh crore, supported by net tax receipts estimated at ₹28.7 lakh crore.
Key Highlights:
- Infrastructure Leap: Public capex has been increased to ₹12.2 trillion, focusing on rare earth corridors and high-speed rail.
- Tax Status Quo: Income tax slabs remain unchanged, but the New Income Tax Act and reduced TCS (2%) on foreign travel offer procedural relief.
- Market Regulation: A sharp hike in STT for F&O aims to discourage retail speculation in the derivatives segment.
- Fiscal Target: The government aims for a 4.3% fiscal deficit, underscoring a commitment to economic stability and debt consolidation.